Abstract
In this assignment, I was tasked with providing a detailed description of any complex item. I chose to describe a video game controller, as it’s something that I use frequently and its interesting to learn about what goes into such complex items that we use in our lives. I provided specific descriptions for each part of the controller with corresponding images and how all the parts work together to create a functioning controller.
Technical Description of Video Game Controller
One of the most common activities that people engage in in their free time is video games. It’s been in almost all of our lives for years, and it definitely won’t stop. However, not many ever question how these video games work, or specifically, the controllers work. A controller is what a player uses to send signals to a console for the game to do an action that the player wants. For example, if a player wants their character to jump in a video game, they would press a button on a controller, and the console would translate that button press into a jump. Of course, there are a plethora of consoles, games, and controllers out there, so there’s a lot of variety to take into consideration. There are multiple controllers that exist, such as the Xbox controllers or PlayStation controllers. However, they all follow the same basic structure of two joysticks, two sets of four buttons on each side, two bumpers, and two triggers on the top. Each company takes the design and cosmetic aspect of the controller in their own way, but the essentials are almost standard across the board. Below are a few different video game controllers, highlighting the subtle differences between each controller (1,2,3). What’s intriguing is all the functions controllers have to do simultaneously. They have to be able to communicate with consoles at almost instant speeds, because competitive games rely heavily on reaction time, and no time can be wasted on communications between devices. Controllers also have to be able to provide comfort for prolonged use and flawless functionality for those competitive games. This is all achieved through the intricate hardware that is built inside.



The hardware that goes inside a controller is much simpler than one would think. All it is is a large circuit board that accepts signals from all the inputs on the controller and then sends those signals to the console, whether it be wired or wireless. In wired controllers, the signal simply travels through the wire to the console, and in wireless controllers, the signal is transmitted either through bluetooth or infrared. However, each input on a controller produces these signals differently. The different types of inputs are buttons, joysticks, and triggers. Firstly, under each button is an incomplete circuit on the circuit board. When the button is pressed, a piece of metal under the button connects the two incomplete ends to make a full circuit, which produces a signal that travels to the console. Below is a picture which shows how each button corresponds to an incomplete circuit on the controller’s circuit board (4). Joysticks, however, are a bit more complicated. Joysticks are sticks with a plastic covering that you can push in any direction to produce an action in the game. 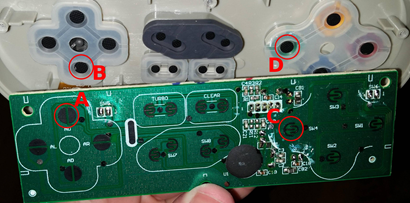 These joysticks are usually associated with movement, or aiming and looking in a specific direction. The way they work is that underneath them is a resistor called a potentiometer. Potentiometers control the current running through them depending on how they are tilted and in which direction. So for example, if the joystick was pushed to the right, the potentiometer would also tilt to the right, producing a signal with a specific voltage that the console detects as the joystick being pushed to the right, and outputs the corresponding action in the game. You can see to the right that the potentiometer somewhat resembles a joystick with the metal piece sticking out, and that’s what is underneath the joystick that tilts in all directions (5).
These joysticks are usually associated with movement, or aiming and looking in a specific direction. The way they work is that underneath them is a resistor called a potentiometer. Potentiometers control the current running through them depending on how they are tilted and in which direction. So for example, if the joystick was pushed to the right, the potentiometer would also tilt to the right, producing a signal with a specific voltage that the console detects as the joystick being pushed to the right, and outputs the corresponding action in the game. You can see to the right that the potentiometer somewhat resembles a joystick with the metal piece sticking out, and that’s what is underneath the joystick that tilts in all directions (5).  Triggers also work in a special way. They can be pressed at varying degrees, causing different actions in the game. For example, if your character has a bow and arrow, a harder press on the trigger means you will pull the arrow further back in the bow, producing a more powerful shot. Inside of these triggers are very small magnets. As they get closer together, they have more resistance because they are opposite poles. This stronger or lighter resistance, depending on how hard the trigger is pressed, produces a signal that then travels to the console. These are all the basic essentials in almost every controller, however a lot of controllers have many features that make it more comfortable or immersive to play.
Triggers also work in a special way. They can be pressed at varying degrees, causing different actions in the game. For example, if your character has a bow and arrow, a harder press on the trigger means you will pull the arrow further back in the bow, producing a more powerful shot. Inside of these triggers are very small magnets. As they get closer together, they have more resistance because they are opposite poles. This stronger or lighter resistance, depending on how hard the trigger is pressed, produces a signal that then travels to the console. These are all the basic essentials in almost every controller, however a lot of controllers have many features that make it more comfortable or immersive to play.
A lot of controllers have a feature called vibration. This is when the controller vibrates rapidly due to an action in-game. Inside the grips of the controllers are motors with an unbalanced weight, as seen below (6).  When the controller is given a signal to vibrate, it runs power through these motors, causing the unbalanced weight to spin. Consequently, the motor tries to balance it, but can’t obviously due to the weight being unbalanced, and so the motor just vibrates creating that vibration effect throughout the whole controller. Some vibration technologies, however, are much more advanced. PlayStation’s new DualSense controller, for example, offers vibration in the form of haptic feedback. This type of vibration is much more precise and immersive, and allows for specific vibrations for specific actions. Haptic feedback uses much smaller motors called voice-coil actuators to produce more accurate vibrations. They have the same essential function, with the unbalanced weight and the motor fighting to balance it, but it offers more precision. These motors are also the same ones used in speakers to vibrate and produce sound, so they are obviously very accurate. Another feature that some controllers have is adaptive triggers. Also in the DualSense controller, adaptive triggers offer resistance in the triggers depending on the activity in-game. For example, when firing a weapon, the trigger can have more resistance depending on the weight and power of the weapon. As seen on the left (7), inside of these adaptive triggers is a gear that pushes against the trigger to create that resistance, and the level of resistance is obviously controlled by the console’s signal sent to the controller.
When the controller is given a signal to vibrate, it runs power through these motors, causing the unbalanced weight to spin. Consequently, the motor tries to balance it, but can’t obviously due to the weight being unbalanced, and so the motor just vibrates creating that vibration effect throughout the whole controller. Some vibration technologies, however, are much more advanced. PlayStation’s new DualSense controller, for example, offers vibration in the form of haptic feedback. This type of vibration is much more precise and immersive, and allows for specific vibrations for specific actions. Haptic feedback uses much smaller motors called voice-coil actuators to produce more accurate vibrations. They have the same essential function, with the unbalanced weight and the motor fighting to balance it, but it offers more precision. These motors are also the same ones used in speakers to vibrate and produce sound, so they are obviously very accurate. Another feature that some controllers have is adaptive triggers. Also in the DualSense controller, adaptive triggers offer resistance in the triggers depending on the activity in-game. For example, when firing a weapon, the trigger can have more resistance depending on the weight and power of the weapon. As seen on the left (7), inside of these adaptive triggers is a gear that pushes against the trigger to create that resistance, and the level of resistance is obviously controlled by the console’s signal sent to the controller.  These are most of the main features that controllers offer today, and they all work using very precise mechanisms inside of the controller.
These are most of the main features that controllers offer today, and they all work using very precise mechanisms inside of the controller.
In conclusion, the gaming controller is a very intricately designed mechanism with a variety of features and functions. All the different buttons, joysticks, and triggers allow the player to input multiple commands for the console to do in the game and give them full control. These different parts all work as efficiently as possible to get the signal out almost instantaneously and allow for smooth gameplay. If any one part fails, the controller as a whole fails, so they all need to function flawlessly. All the features that they provide, such as vibrations and adaptive triggers, allow for a more comfortable and immersive feel, and work alongside the inputs detected by button presses and joystick movements to create the experiences that the companies promise the players.
Works Cited
Sources:
“How Game Controllers Are Made.” TOMORROW’S WORLD TODAY®, 28 Dec. 2020, www.tomorrowsworldtoday.com/2018/12/21/how-game-controllers-are-made/.
Jones, Camden. “PS5 Controller: What Haptic Feedback Actually Does.” ScreenRant, 13 Apr. 2020, screenrant.com/ps5-controller-what-haptic-feedback-actually-does/.
“Potentiometer: Resistor Types: Resistor Guide.” EEPower, eepower.com/resistor-guide/resistor-types/potentiometer/#.
Spiers-Unwin, Ruby. “PS5 Controller Teardown Reveals How Adaptive Triggers Work.” The Loadout, The Loadout, 5 Nov. 2020, www.theloadout.com/ps5/controller-teardown#:~:text=A%20plastic%20corkscrew%2Dshaped%20gear,game%20weapon%2C%20and%20much%20more.
Wilson, Mark. “What Is a Voice Coil Actuator.” MachineDesign, 24 Apr. 2018, www.machinedesign.com/mechanical-motion-systems/article/21836669/what-is-a-voice-coil-actuator.
Images Sources:
- PlayStation
- GameStop
- Walmart
- Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange
- Analog IC Tips
- Amazon
- Screen Rant

